Optical fiber cables are crucial for modern telecommunications, offering high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal loss and interference. Among the various types of optical fiber cables, the GYTA and GYTS cables are commonly used in various applications due to their specific characteristics. This article explores the appropriate use cases for GYTA and GYTS cables, along with the key considerations in their production and installation.
1. Overview of GYTA and GYTS Optical Fiber Cables
1.1 GYTA Optical Fiber Cable
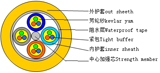
The GYTA cable is an outdoor optical fiber cable designed for use in various environmental conditions. Its full name is "Optical Fiber Cable with a Central Tube and a Loose Tube Structure." It is characterized by a central loose tube that contains optical fibers, surrounded by strength members and protective layers.
Key Features:
-
Structure: Central tube with loose tubes, providing protection to individual fibers.
-
Strength Members: Typically made of steel wires or other high-strength materials.
-
Protective Layers: Includes an outer sheath made of materials like PVC or PE for protection against environmental factors.
1.2 GYTS Optical Fiber Cable
The GYTS cable is also an outdoor optical fiber cable, known as "Optical Fiber Cable with a Central Tube and a Steel Tape Armored Structure." It is designed for rugged conditions where additional mechanical protection is necessary.
Key Features:
-
Structure: Central tube with loose tubes, similar to GYTA.
-
Armoring: Steel tape armor for enhanced protection against physical damage.
-
Protective Layers: Includes a water-blocking layer and an outer sheath for additional protection.
2. Applications of GYTA and GYTS Cables
2.1 Applications of GYTA Cables
2.1.1 Urban and Suburban Networks
GYTA cables are well-suited for urban and suburban environments where physical damage risks are lower but environmental factors such as moisture and temperature fluctuations need consideration. They are used in:
2.1.2 Industrial and Commercial Buildings
In commercial and industrial settings, GYTA cables are often used to connect different buildings or facilities within a campus. Their ability to withstand typical environmental conditions makes them ideal for:
-
Office Complexes: Interconnecting office buildings and data centers.
-
Manufacturing Facilities: Linking control systems, sensors, and data collection points.
2.2 Applications of GYTS Cables
2.2.1 Harsh Environmental Conditions

GYTS cables are designed for environments where additional protection is required due to potential physical threats. Their steel tape armor provides enhanced durability, making them suitable for:
-
Outdoor Installations: Exposed to potential mechanical stress, such as construction sites or along roadways.
-
Underground Installations: Where physical protection is crucial due to potential digging or heavy machinery.
2.2.2 Long-Distance Transmission
For long-distance transmission where additional protection against external factors is necessary, GYTS cables are used:
3. Manufacturing Considerations
3.1 Manufacturing GYTA Cables
3.1.1 Material Selection
-
Optical Fibers: Choose high-quality fibers with low attenuation and minimal dispersion.
-
Loose Tubes: Typically made from high-strength plastic to house the fibers securely.
-
Strength Members: Steel wires or aramid fibers are common, providing the necessary tensile strength.
-
Outer Sheath: The choice of material (PVC, PE) depends on the environmental conditions where the cable will be used.
3.1.2 Production Process
-
Tube Assembly: Fiber strands are placed inside loose tubes, which are then filled with gel or other protective materials.
-
Armoring (if applicable): For GYTS cables, steel tape is applied around the tube to provide additional protection.
-
Sheathing: The outer layer is applied, ensuring that the cable is fully protected from environmental factors.
3.2 Manufacturing GYTS Cables
3.2.1 Material and Structure
-
Armoring Materials: Steel tape is used to provide physical protection. Ensure proper corrosion resistance.
-
Water-Blocking: Incorporate water-blocking materials to prevent moisture ingress.
-
Sheath Material: Choose materials that can withstand harsher environmental conditions, such as PE or specialized compounds.
3.2.2 Quality Control
-
Testing: Conduct rigorous tests for tensile strength, attenuation, and environmental resistance.
-
Inspection: Regularly inspect the manufacturing process to ensure consistency and quality.
4. Installation Considerations
4.1 Installing GYTA Cables
4.1.1 Site Preparation
-
Trenching: Ensure trenches are properly dug to avoid damaging the cable.
-
Environmental Factors: Consider temperature, moisture, and potential for chemical exposure.
4.1.2 Handling and Deployment
-
Cable Handling: Avoid excessive bending or twisting during installation.
-
Splicing: Use proper techniques and equipment to splice fibers, ensuring minimal loss.
4.1.3 Protection
-
Conduit Use: For additional protection, especially in urban environments, use conduits to house the cables.
-
Markers: Place markers along the installation path to indicate the presence of the cables.
4.2 Installing GYTS Cables
4.2.1 Site Preparation
-
Rugged Terrain: Prepare for more challenging installation conditions, such as rocky or unstable soil.
-
Protection Measures: Use additional protective measures, such as steel conduit or additional armoring, where required.
4.2.2 Handling and Deployment
4.2.3 Safety and Compliance
5. Conclusion
Both GYTA and GYTS optical fiber cables play crucial roles in modern telecommunications, each suited to specific environments and applications. GYTA cables are ideal for urban and commercial settings where environmental conditions are moderate, while GYTS cables excel in harsh environments requiring additional physical protection. Understanding their respective advantages and considering key manufacturing and installation factors ensures the optimal performance and longevity of these essential components in network infrastructure. Proper attention to material selection, production quality, and installation practices will lead to a more reliable and efficient optical fiber network.